designpicture booksmovieprocess
previous1234next
5. How do experts take care of children actually?
Through the interview to a pediatrician, a clinical psychologist, a childcare worker and a mother of a child, I found out some points which could be improved. Especially, since I agreed to the opinion from the pediatrician that, in order to reduce the anxiety of children in hospital, it would be more effective to focus on the most concerned three points by children, such as‘whether the treatment finishes soon’,‘whether it is painful’ and ‘whether the parents can be together or alone’, and then express more specific examinations or treatments that children would have actually. I decided to pick up four kinds of medical examinations which child patients in hospital receive mainly (CT, X-ray, Echo and ECG). How are the examinations and the treatments actually performed for children in hospital, and how are the children looked after there? In order to know more about them, I decided to visit the Beatrix Children’s Hospital of Groningen University in the Netherlands.
Visits to the Beatrix Children’s Hospital of Groningen University
The Groningen University Hospital is located in the northern part of the Netherlands, and there, about 17000 people are working. In the pediatric ward, almost 700 personnel are working. Eleven of them are hospital play specialists, two are hospital clowns. There are also some volunteers who look after the daily life of children in the hospital.
Playmate and places to play in the hospital: At the play room, volunteers are playmates of child patients. In the radiotherapy department, there is no play room for children.
At the Beatrix Children’s Hospital, I asked the play therapists to show their actual activities at hospital. When I visited a playroom, a volunteer woman was reading a picture book for a child patient. The volunteers of the pediatric department support hospital play specialists who are likely to be too busy with the care of serious cases to take care of all child patients. The volunteers help play-specialists in the possible range, such as playing with children in a playroom. There, children themselves can choose what they want to play such as toy blocks and board games. They can also ride on a small bicycle there. Volunteers make it a rule to play with children only when they are asked for.
Basically, parents are allowed to attend every examinations and treatments of their children, if their physical conditions are suitable. Mainly, the child patients can play in the waiting rooms of pediatrics, playrooms or sickrooms, although it depends on their physical conditions and purpose of visit. In case of the medical diagnoses of radiology, children have to move to the department of radiology mainly used for adults, in order to have examinations by the precision instruments. In the department, however, there are no particular places for children to play. Therefore, the play-preparation is performed in the pediatric ward or at a certain place available at the time. Children who undergo a MRI test are asked to come to the hospital about half hour before the treatment in order to receive the play-preparation with a special DVD video.
Toys for hospital play preparation
Hospital Play Specialists explain medical treatments in an enjoyable manner, even if it is about having an intravenous drip. Also, letting children perform in the same way is the key to develop a positive mind-set in them.
Ms. Mirjam van Gent, the head of social workers and volunteers at the hospital showed me how she was usually giving explanations of the medical diagnoses and the treatments to children. She showed me how she tells about intravenous drip or patches of electrocardiogram. It was a performance with dolls and I was impressed by her unserious manner to let children do it like fun and play. She always firstly shows how the procedure will be done to children, and secondly gets children do in the same way she did. Like this, if children can simulate treatments or operation that they will receive, they can be positive to receive them.
 Ms. Mirjam explains medical examinations with the actual instruments such as intravenous drip or patches of electrocardiogram. Her purpose is to explain about medical treatments, but her performance did not look serious, and it looked rather fun like a part of usual children’s play. It was an idea to encourage children to overcome hardship positively by showing the situation enjoyable.
Ms. Mirjam explains medical examinations with the actual instruments such as intravenous drip or patches of electrocardiogram. Her purpose is to explain about medical treatments, but her performance did not look serious, and it looked rather fun like a part of usual children’s play. It was an idea to encourage children to overcome hardship positively by showing the situation enjoyable.About the toys that had been commercialized for hospital play-preparation: If there are tools that could be used easily by hospital staffs, more hospitals will be able to practice hospital play preparation.
I asked Ms. Mirjam and her colleagues about their opinions on the tools that had been developed for the hospital play preparation. For example, the Philips Healthcare based in the Netherlands had already made a play-preparation tool called Kitten Scanner for children who are to undergo a medical CT scan. She told me that the Kitten Scanner was too expensive to purchase within their budget and it would be quite large to install. It also seemed that there was no easy way for this hospital to introduce these supplementary products of Philips since the hospital was already using the instruments produced by other medical equipment manufacturer. In regard to the tools, purposefully made for play-preparation, she told that only a DVD video for the MRI test had ever been used by them, and that they were hoping to use this kind of tools appropriately for other kinds of diagnoses, too.
A doubt about the miniature models for hospital play preparation: Would it be better if we have the toys that make children want to play?
After the visit to the Beatrix Children’s Hospital, I found that not only the Philips Healthcare but other manufacturers were producing models for the play-preparation. They are reduced scale models of medical equipment for the purpose of explanation to children about the examinations. However, when I remember the basic concept of the play-preparation learned at the Astrid Lindgren Children’s Hospital that ‘children can increase their own consciousness and independency by playing on their own will’ such miniature models lacked attraction for children to play with because their purpose was limited to the use of explanation by doctors. Medical equipment such as CT scan is not familiar with children, so I thought the play-preparation toys should be more attractive in some way so as to encourage children to try, explore, and discover more.
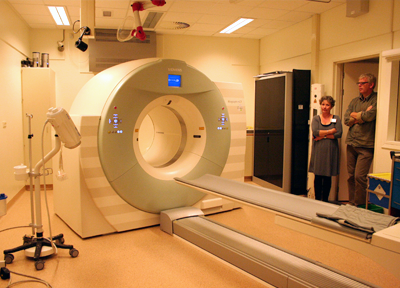 A Computerized tomography scanner (CT scan) Beatrix Children’s Hospital has the largest operation ward for pediatrics in the Netherlands. So, the precision examinations for children are done very frequently. In order to have examinations by the precision instruments, children have to move to the department of radiology mainly for adults.
A Computerized tomography scanner (CT scan) Beatrix Children’s Hospital has the largest operation ward for pediatrics in the Netherlands. So, the precision examinations for children are done very frequently. In order to have examinations by the precision instruments, children have to move to the department of radiology mainly for adults. 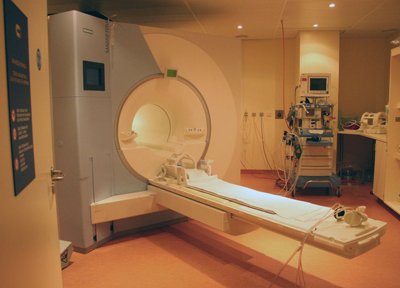 MRI room
MRI room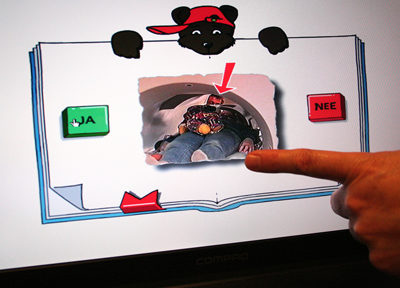 This hospital is using a special DVD video as a preparation tool for the MRI test. The DVD consists of a movie about the process of MRI examination and some simple quiz games about them. Through the video, children can image the situations such as the tunnel on the MRI machine is very narrow, the machine generates strong magnetism, big buzzer sounds will be heard continuously during the examination and their head will be fixed to the bed.
This hospital is using a special DVD video as a preparation tool for the MRI test. The DVD consists of a movie about the process of MRI examination and some simple quiz games about them. Through the video, children can image the situations such as the tunnel on the MRI machine is very narrow, the machine generates strong magnetism, big buzzer sounds will be heard continuously during the examination and their head will be fixed to the bed. 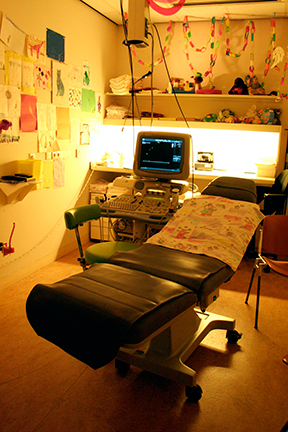 In the treatment room, many dolls and pictures are displayed in order to distract children’s tension.
In the treatment room, many dolls and pictures are displayed in order to distract children’s tension.5.実際の現場ではどのように子供をケアしているのか?
小児科の医師、臨床心理士、保育士、子供の母親へのインタビューを通じて、改善の余地のあるポイントをいくつか掴むことができました。特に小児科の医師からの「病院での子供の不安を取り除くには、病院全体で起こる様々なことを漠然と描くよりも、本当に子供が気にしている、すぐ終るのか、親も同伴するのか、痛みをともなう処置なのかという3点にフォーカスし、子供達が実際に関わる具体的な検査や処置について表現するほうが効果的だ」という意見に納得したため、形にする対象を子供が病院で受ける主な検査であるという4種類(CT検査, X-rayレントゲン撮影, エコー、心電図)に絞って考えることにしました。では一般的な病院では、これらの検査や処置は実際どのように行われており、どのようなケアがこどもたちにされているのか?それを知るため、私はオランダのフローニンゲン大学ベアトリクス子供病院を訪問することにしました。
フローニンゲン大学ベアトリクス子供病院の訪問
フローニンゲン大学病院は17000人の職員が働く、オランダの北に位置する病院です。小児病棟には700人の職員がおり、そのうちの11人のホスピタル・プレイスペシャリストや2人のホスピタルクラウン、ボランティアが子供の院内での生活をサポートしています。
病院での遊び相手と遊び場所
プレイルームではボランティアの人達が遊び相手となる。放射線科には子供用のプレイルームはない。
ベアトリクス子供病院で、私はプレイセラピストの実際の活動を見せてもらうことができました。私がプレイルームを訪れた時、ボランティアの女性が入院中の子供に絵本を読んであげている最中でした。小児病棟のボランティアは、重病患者のケア等で多忙となるプレイスペシャリストを助ける存在で、彼らは主にプレイルームで子供の遊び相手になるなど、可能な範囲での手伝いを行っています。プレイルームには、ブロックやボードゲーム、子供用の自転車などもあり、子供達は自分の遊びたいもので遊べるようになっています。ボランティアは子供達から必要とされた場合に一緒に遊ぶようにしています。
検査や処置の際、親は自分の体調次第で、自分の子供のどの検査、治療にも立ち会えることになっています。子供の様態や病院の訪問の目的によって異なりますが、病院での子供の遊び場は、主に小児科の待合室、入院病棟のプレイルーム、病室になります。CTなどの放射線系検査の場合は、子供の患者は大人の患者が利用する放射線科に移動して検査を受けることになります。この病院の放射線科には、特別な遊び場は用意されていないため、プリパレーションは小児病棟または、利用出来るスペースを見つけて行うことになります。MRIの場合は、検査を受ける子供に検査本番より約30分前に来てもらい、DVDビデオでのプリパレーションを行ってから検査を行っているそうです。
ホスピタルプリパレーション用のおもちゃ
点滴の装着も、楽しげなパフォーマンスで説明する。子供にも同じく演じてみさせることが、前向きな気持ちを持たせるための鍵となる。
ベアトリクス子供病院のソーシャルワーカー(プレイスペシャリストの役割)とボランティアグループのヘッドであるミリヤムさんに、普段どのように子供達に処置や検査の説明を行っているのか見せてもらいました。 彼女は点滴を装着する時の説明などを見せてくれましたが、それは堅苦しいものではなく、人形を使ったパフォーマンスのようなものでした。ミリヤムさんは、いつも最初にどのような処置であるのか子供にパフォーマンスで見せ、その後子供にも同じ人形を使って演じさせてみます。そのように、こども自身が自分に行われる手術や処置をシミュレーションしてみることで、それらに対して前向きな気持ちを持てるようになるそうです。
・ミリヤムさんによる点滴や心電図のパッチなど、実際に使用する器具をつかって検査の説明。説明といっても、堅苦しいものではなく楽しいもので、こどもが普段やっている遊びの延長のようだった。辛い事も、楽しく演出することで、ポジティブな気持で乗り越えられるようにする工夫である。
商品化されているプリパレーション用おもちゃについて
容易に導入できるツールがあれば、より多くの病院がプリパレーションを実践できるようになるのでは?
既に開発されているプリパレーションの道具についてミリヤムさんたちに意見を伺いました。例えば、オランダのフィリップス・ヘルスケアでも、MRIやCT検査用の子供のプリパレーションツールが開発されているのですが、それらは設備として大掛かりで価格的に高く導入しにくいことでした。病院がこれらの設備を取り入れにくいのは、病院が使用している実際の検査機器が他社の製品であるため、導入するルートがないということもあるようでした。プリパレーション用の特別な道具としては、この病院ではMRI検査用に作られたDVDが使われていますが、MRI以外の検査、処置に対してもそのような簡単に導入できるものが欲しいとのことでした。
プリパレーション用の模型に感じる疑問
子供が自ら遊んでみたくなるプリパレーション用のおもちゃがあっても良いのでは?
その後、フィリップスに限らず、プリパレーション用の検査機器の模型は他でも販売されていることを知りました。それらは、機器のミニチュア版であり、主に医師が子供へ検査を説明するために作られた形のものでした。しかし、子供は自らの意志で遊ぶことで自身の意識や自主性を高めることができるという、スウェーデンのアストリッド・リンドグレーン子供病院で行われているプレイプリパレーションの基となっている考えから見直すと、それらは子供達が自ら遊び始めたくなるような、子供を楽しませる魅力を伴っていないように感じました。CTなどの医療機器は、本来は子供にとって親しみの無いものであるため、子供が自然と興味を持ち、触りたくなるような工夫が必要ではないかと思いました。
・CT装置。ベアトリックス病院にはオランダ最大の小児手術棟があり、こども患者の精密検査も頻繁に行われている。放射線科の検査を受ける時、子供患者は子供病棟から大人も利用している放射線科へ移動する。
・この病院ではMRI検査のプリパレーションにDVDビデオを使っている。DVDは子供が検査を受けるプロセスの映像と、検査に関する簡単なクイズで構成されている。これを見ることで、MRI検査中に大きなブザー音が鳴り続けることや検査機のトンネルの穴が非常に小さい事、検査機が強い磁力を発生すること、検査中に頭が固定されることなどの状況をイメージすることができる。
・処置室。子供の気を紛らわすための人形や絵が沢山飾られている。
previous
1
2
3
4
next